Masotherapy.
La massage therapy It is one of the oldest physiotherapeutic treatments known. It is a combination of varied manoeuvres, based on movement and pressure, applied to the body and with therapeutic objectives.
When applying the massage we can do it at 3 levels deep:
- Superficial: it is carried out with a minimum intensity, it acts on the skin and the subcutaneous tissue.
- Medium: a greater intensity is applied, acting on the superficial and middle musculature. It is the most used.
- Deep: maximum intensity to reach the deepest muscles. It is usually used in the sports field.
TENS .

El TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation), is a device commonly used in physiotherapy, which works on the pathways that transmit pain, producing a analgesic effect or a modulation of affected sensitivity.
The physiological basis on which TENS is based is the “ work de gate of the pain”. This basis supports the fact that the brain can control pain by closing or opening the pathways through which it is transmitted. This is done unconsciously, but with TENS an external way of controlling this transmission of pain has been found.
In addition, TENS takes into account the accommodation capacity of the brain, which is why in the same session it produces variations of intensity and frequency that stimulate the brain constantly to relieve pain.
Radiofrequency R-200.
El physiotherapy treatment accompanied by radiofrequency health professional, in our case the R-200 (also known as diathermy), consists of the emission of electromagnetic radiation that reaches the most internal tissues, producing an increase in temperature in them.
This increase in temperature is between 3º and 4ºC and is not produced by the machine, but by the body itself, in response to the movement of electrical charges in the current that reaches the interior of the cells.

Kinesitherapy.
- Improves circulation, venous and lymphatic return.
- Increased muscle tone and muscle power, especially in resisted exercises.
- Helps to have more lax joints and improve mobility. With this we avoid stiffness and adhesions.
- Improves coordination, balance and proprioception.
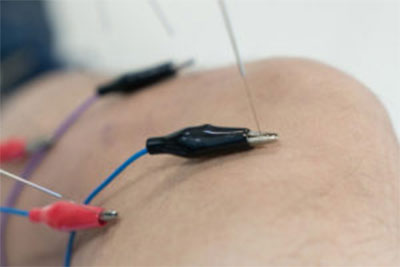
dry needling.
"Dry needling" is a physiotherapy technique based on the use of a needle to stimulate trigger point receptors or muscle contractures. With this we relax the muscle and increase its elasticity.
All muscles have a series of trigger points that are usually inactivated but on certain occasions due to various circumstances they activate and produce local or radiated pain.
We can differentiate a trigger point from a contracture by the type of pain. Generally, the contracture will appear with localized pain in the area and in the case of the trigger point it normally develops with radiating pain; a typical example is the pain that reaches us from the neck to the head.
The causes that can activate these points or develop contractures are multiple: an overload, repetitive movements in daily life, lack of laxity and elasticity, a sudden fall or blow, poor posture...
During the dry needling treatment, the physiotherapist manipulates the needle several times, depending on the condition and muscle response, until relaxation is achieved.
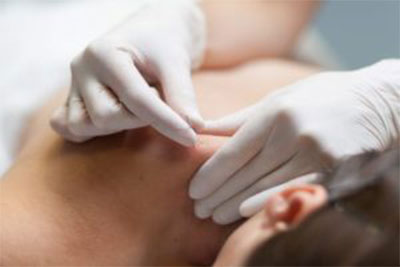
Electroneuroacupuncture.
La Electroneuroacupuncture (ENA) is a recently developed technique in the physiotherapeutic field that integrates the concepts of acupuncture/Chinese medicine with neuromodulation.
We give an anatomical and clinical view of the meridians that run through the body and their most prominent acupuncture points. This vision of pathology globally teaches us to visualize the whole and not focus on a point or affected area and thanks to this we can treat all kinds of pathologies, whether they are chronic, acute, physical or emotional.
With the combination of these two techniques already known in physiotherapy, we found the perfect union of an invasive therapy based on nerve innervation and anatomical points (neuromodulation) that integrates perfectly with traditional Chinese medicine and its points in the meridians that run through our body (acupuncture).
Kinesiotaping .
Functional taping is a type of physiotherapeutic technique which consists of limiting, inhibiting a movement that causes pain, leaving the rest of the movements free. In this way, only the structures that are damaged remain at rest and we avoid the drawbacks of complete immobilization (loss of muscle mass, risk of loss of bone density in the immobilized region, circulatory problems, thromboembolism, and other unwanted effects). Functional bandages can be preventive or therapeutic.
Necessary material:
- Foam (Protection plates)
- pre-sold
- adhesive spray
- Elastic bandages
- Tape
- Scissors

functional bandage.

- Foam (Protection plates)
- pre-sold
- adhesive spray
- Elastic bandages
- Tape
- Scissors
Auriculotherapy.
La Auriculotherapy It is a technique within the field of painless alternative medicine, it was originally created to treat stress and anxiety but that currently progress has been made in its study and covers the treatment of dozens of pathologies, currently being a widely used technique in physiotherapy.

Suction cups.
La cupping Technique, better known in the field of physiotherapy as the cupping technique, despite the fact that it has been used for thousands of years by traditional Chinese medicine, it has not been very popular until in 2016, at the Olympic Games in Rio de Janeiro, where the technique has become widely known and used, as a result of of seeing some athletes on television with "marks" on their backs as a result of having been treated with this cupping technique.

El physiotherapy treatment with this technique consists of its application on certain parts of the body, with which the skin and part of the muscle are sucked, obtaining a vacuum, so that the pores open and thus promote blood and lymphatic circulation.
The original method that was used, although it is still being done today, consists of the use of glass suction cups, where a cotton swab with alcohol hooked with tweezers is used, it is lit and this combustion of oxygen is what generates the vacuum and sucks the skin .
Moxibustion.

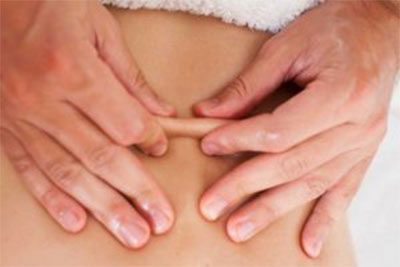
Myofascial Release.
Lymphatic drainage.
El manual lymphatic drainage is a massage therapy technique in physiotherapy very soft, slow and repetitive movements on the skin, which must be done in the right direction to help improve the lymphatic system.
El lymphatic system It consists of a series of capillaries or ducts where waste products from other tissues are collected and transported to the circulatory system, so that the body can get rid of these wastes. When the lymphatic system is not capable of eliminating these wastes, edemas or retentions appear. Along the course of the lymphatic system are the lymph nodes, which are responsible for purifying pathogens. These become inflamed because they cannot purify when the lymphatic system is affected.

Ultrasound.
El ultrasound physiotherapy treatment, consists of a treatment based on the mechanical vibrations of a longitudinal wave that produces compressions in the tissue. Ultrasound requires a special medium for its application, through which these waves can be transmitted. This medium is commonly referred to as "ultrasonic conductive gel."

The frequency at which we will use ultrasound will depend on the pathology:
- High frequencies: 3Mhz, for superficial pathologies.
- Low frequencies: 1Mhz, for deeper pathologies.
The tissues with a better response to this type of waves are those with a high amount of collagen and absorption: tendons, ligaments, joint capsule and fascia.
It is therefore a therapy to be used in both acute and chronic cases, it will only depend on the parameters with which we use. Also, being a painless therapyIt is very pleasant for the patient.